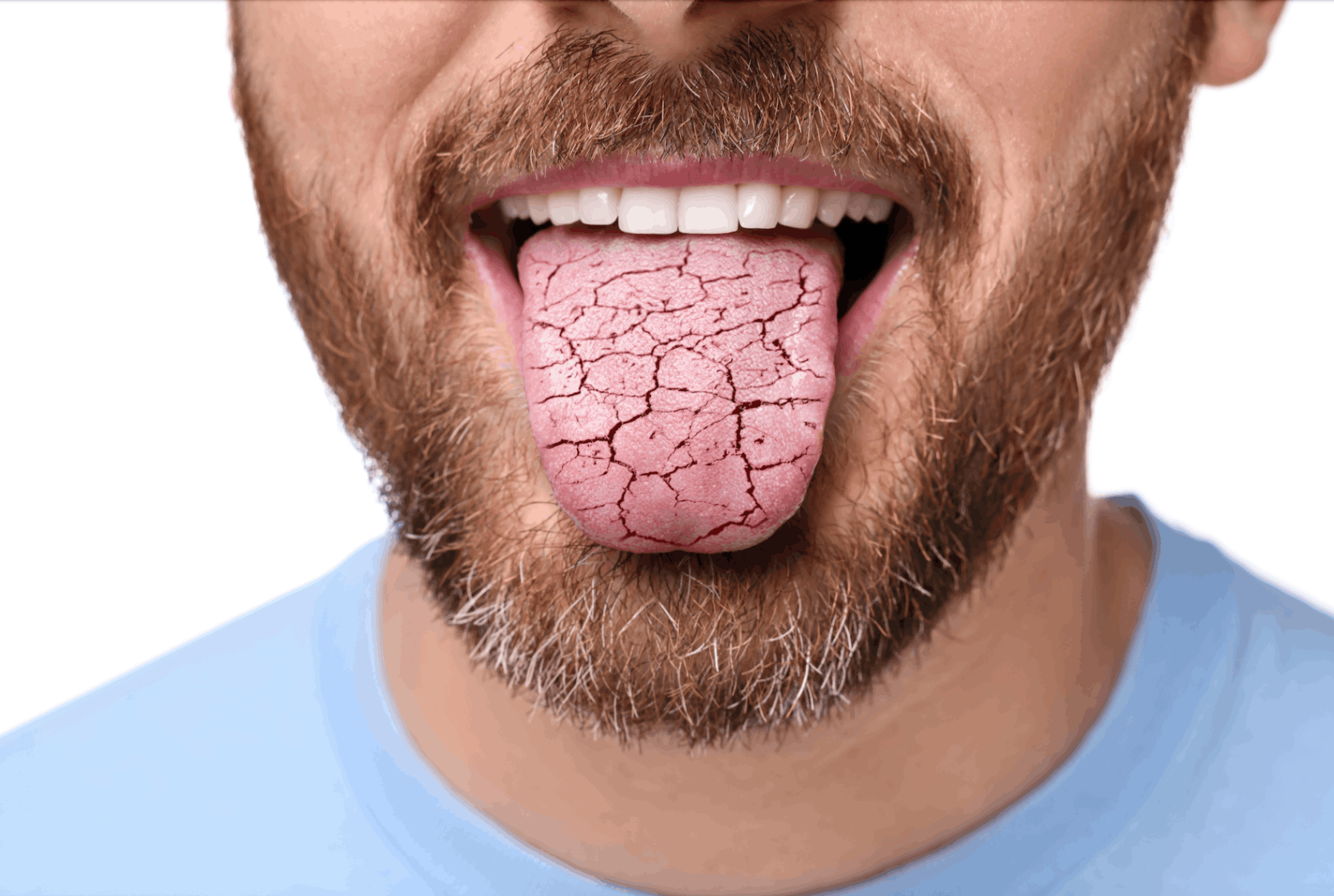
Xerostomia
What is Xerostomia?
Xerostomia is a subjective sensation of dry mouth, associated with a decrease in saliva production by the salivary glands, even though they can maintain their normal function. This condition can cause inconvenience and reduce quality of life, and can lead to or be indicative of other health problems, so it shouldn't be ignored. It is therefore important to always get a diagnosis from a qualified health professional in order to identify xerostomia, understand the possible causes and carry out the appropriate treatments.
Saliva plays a crucial role in oral health, aiding digestion, verbal communication, keeping the mouth clean and protecting the oral cavity and the body against pathogens.
Maintaining good hydration, adopting healthy eating habits, using products specially formulated to relieve dry mouth and seeking professional help when necessary are fundamental steps to treat and prevent it.
Xerostomia can be a symptom of various medical conditions or a side effect of certain medications. Effective treatment depends on identifying the underlying cause and implementing appropriate measures to relieve symptoms.
Possible Symptoms
Feeling of Dry Mouth and Throat
The main characteristic of xerostomia is a persistent feeling of dryness in the mouth and throat, which can make it difficult to speak, swallow or wear dentures.
Thick or Sticky Saliva
Saliva can become thick or sticky, which can be uncomfortable and make
chewing,
speaking and
swallowing
difficult.
Cracks in the labial commissures (corners of the mouth) and lips
Constant dryness can lead to cracked lips and commissures, which can be painful and are vulnerable to infection.
Dry and Irritated Gums
The gums can become dry, irritated and more susceptible to gum disease.
Bad Breath
(Halitosis)
Saliva helps to clean the mouth and eliminate bacteria. A lack of saliva can result in persistent bad breath.
Rough, cracked tongue sensation
Altered or reduced taste
Xerostomia can affect the sense of taste, resulting in an altered or unpleasant taste in the mouth.
Increased Risk of Tooth Decay and Oral Infections
Xerostomia increases the risk of tooth decay, fungal infections such as candidiasis and other oral conditions.
Available Treatments
Treatment depends on the underlying cause. However, one of the main aims of treatment is to ensure symptom management and prevent complications.
Adequate Hydration:
Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps keep your mouth moist and can relieve the symptoms of dry mouth. Staying hydrated is essential for general and oral health.
Stimulation of Saliva Production:
Chewing sugar-free gum can stimulate the salivary glands to produce more saliva.
Use of Saliva Substitutes:
Products such as gels, sprays and mouthwashes specially formulated to moisturize the mouth can provide temporary relief. These saliva substitutes help to lubricate the mouth and reduce the sensation of dryness.
Oral Hygiene Care:
Good oral hygiene with suitable products, usually containing lactoperoxide, lysozyme and lactoferrin. It is essential to ensure regular brushing and flossing, and to keep regular appointments with the dentist or oral hygienist at least every six months.
Avoid Dehydrating Substances:
Avoid alcohol, caffeine, tobacco and very salty or spicy foods, as they can worsen the sensation of dry mouth. These substances can further dehydrate the mouth and make symptoms worse. It is very important to maintain a healthy diet with water-rich fruit and vegetables.
Use of Humidifiers:
Using a humidifier in the bedroom at night can help reduce dryness in the mouth and throat. This is especially useful in dry climates or during the winter.
Medication: Drugs such as pilocarpine can also be prescribed to help stimulate saliva production;
Consultation with a Dentist:
A healthcare professional will help identify the underlying cause of xerostomia and recommend appropriate treatments. In some cases, adjustments to medication or treatment of underlying medical conditions may be necessary. In addition, it may be necessary to discontinue or change the medications or dosage that are part of daily therapy.
Our Clinical Team is here to help you!
Agreements and Partnerships
FAQ's
1. What causes xerostomia?
Xerostomia can be caused by various conditions, including the use of certain medications, medical treatments such as radiotherapy of the head and neck, autoimmune diseases such as Sjögren's Syndrome, diabetes, Parkinson's Disease, Hepatitis C, HIV, disorders of the Nervous System, Graft versus Host Disease, dehydration, damage to the salivary glands. Lifestyle and mouth breathing can also cause dry mouth.
2. But how is xerostomia diagnosed?
Diagnosis usually involves a series of steps to determine not only its origin, but also the most appropriate treatment. The process of diagnosing xerostomia therefore involves:
- Adequate clinical history, including gathering information on family history, medical and dental history, medication;
- Clinical oral examination;
- Measurement of the salivary flow rate - the amount of saliva produced per minute;
- Clinical analysis to screen for possible underlying diseases;
- Imaging examinations of the salivary glands, looking for morphological changes, such as the presence of salivary calculi.
3. How can I relieve dry mouth at home?
Drinking plenty of water, chewing sugar-free gum, avoiding alcohol and caffeine, and using saliva substitutes can help relieve the sensation of dry mouth. Maintaining good oral hygiene is also important to prevent complications.
4. When should I see a dentist to treat xerostomia?
If the sensation of dry mouth is persistent, severe or accompanied by other symptoms, it is important to see a dentist. Xerostomia can increase the risk of tooth decay and oral infections, so a professional assessment is essential.
5. Is xerostomia a sign of a serious medical condition?
In some cases, xerostomia can be a symptom of underlying medical conditions such as diabetes, Sjögren's Syndrome or autoimmune diseases. If xerostomia persists, it is important to see a healthcare professional for a full assessment.
6. Can children have xerostomia?
Yes, children can also have dry mouth, usually due to the use of certain medications or respiratory conditions. Adequate hydration and good oral hygiene are essential to prevent complications.
7. Does smoking cause xerostomia?
Yes, tobacco can cause dry mouth by reducing saliva production, both because of its chemical composition and because of the heat it generates. Its vasoconstrictive effect will reduce irrigation to the salivary glands and alter their function.
8. Are oral elixirs effective against xerostomia?
Some oral elixirs specially formulated for moisturizing can help relieve dry mouth. It's important to choose alcohol-free products. Ask your oral health professional for advice.
9. Can xerostomia be treated with diet?
Certain dietary adjustments can help reduce dry mouth. Consuming foods rich in water, such as fruit and vegetables, and avoiding foods that are too salty or spicy can be beneficial.
10. Can xerostomia be caused by anxiety or stress?
Yes, stress and anxiety are present in 80% of dry mouth cases. Stress management techniques can help relieve xerostomia.
11. What are the complications of xerostomia if left untreated?
If left untreated, xerostomia can:
- Hinder the chewing process, which can have nutritional and therefore systemic consequences.
- Increase the risk of tooth decay and periodontal disease;
- Increase the risk of fungal infections, such as candidiasis;
Our Clinical Team is here to help you!